On average, every day 480 Canadians are diagnosed with diabetes, more than 20 Canadians die of diabetes-related complications, and 14 Canadians have a lower limb amputated due to diabetes. Could you have diabetes and not know it? It is important to know whether you have diabetes, because if you are aware of it, you can take steps to manage your condition and lead a healthier life. However, if left untreated, diabetes can cause very serious complications.
Different types of diabetes
There are several different types of diabetes:
• Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which the body’s immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, making the affected people dependent on injecting insulin into their bodies. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children and youths, but it can occur in adults as well.
• Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the body cannot properly use the insulin it produces. In some cases, type 2 diabetes can be managed with oral medication, but some people with type 2 will need to inject insulin.
• Gestational diabetes may develop during pregnancy if a woman’s blood sugar reaches too high a level. It usually disappears following delivery of the baby, but it increases the woman’s chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
What causes diabetes?
There is a lot of misinformation about diabetes floating around. For example, diabetes is not caused by eating too much sugar, and people do not give themselves diabetes. The causes of diabetes depend on the type of diabetes the person has—type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes. Among the possible causes are your genes, family medical history, ethnic background, and your general health.
Symptoms
Some people with diabetes don’t experience any obvious warning signs, but those who do may have some of the following symptoms:
• cuts and bruises that are slow to heal
• lack of energy or extreme fatigue
• frequent or recurring infections
• unusual thirst
• frequent urination
• tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
• trouble achieving or maintaining an erection
• blurred vision
• weight loss or weight gain
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood glucose (blood sugar) levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Nearly six million Canadians have prediabetes. If left untreated, prediabetes can develop into type 2 diabetes. If you have prediabetes, taking steps to manage your blood glucose levels can help prevent you from developing diabetes.
Managing blood glucose
There are several measures you can take to help manage your blood glucose levels:
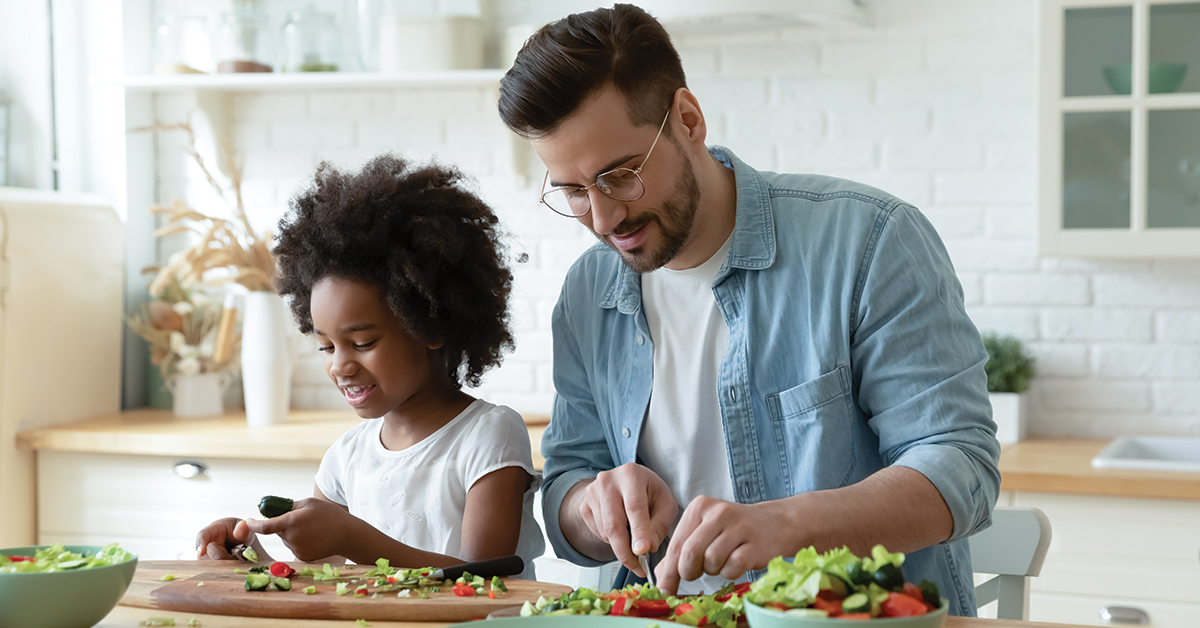
• Eat a healthy diet
• Be physically active
• Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight
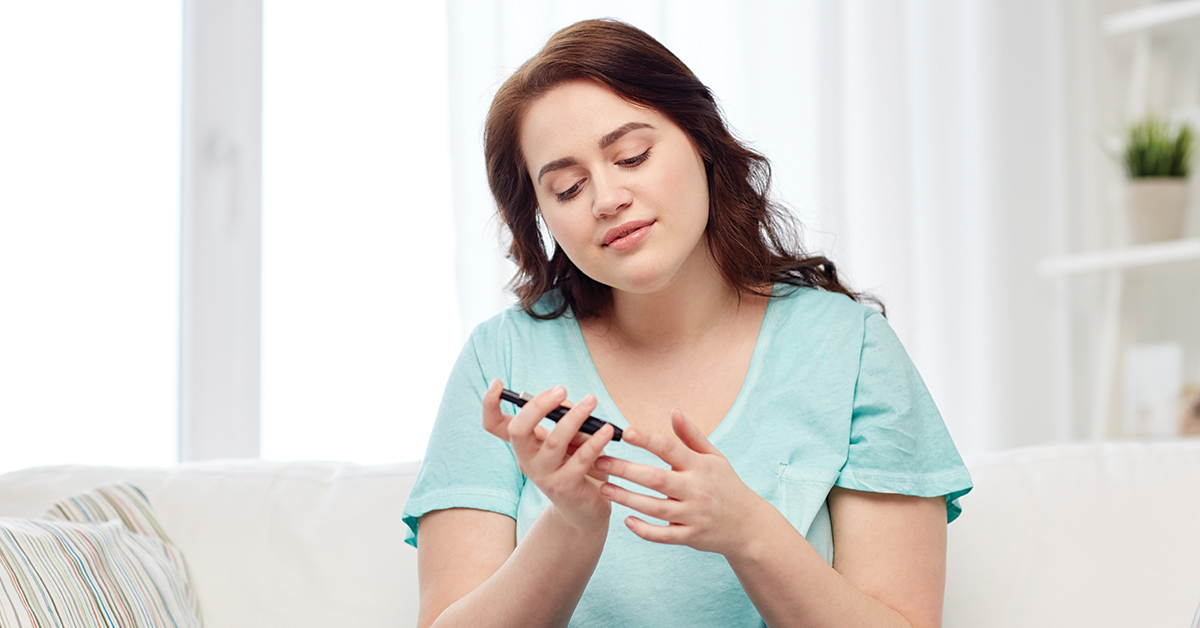
• Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly
• Take any medication your doctor prescribes exactly according to the directions
Diagnosing diabetes
If you think you or someone you know may have diabetes, seek medical attention as soon as possible, so you can begin managing the condition and prevent complications. There are several tests used to diagnose diabetes:
• Fasting blood glucose test
• Random blood glucose test
• A1C test
• Oral glucose tolerance test
While diabetes cannot be cured, it can be managed, and people with diabetes can lead happy, fulfilling lives. Diabetes Management Clinics are also available at London Drugs for one-on-one consultations.
Read other articles in our Fall-Winter 2021 volume of our Bettercare magazine here or learn more about the Diabetes services offered at London Drugs.